Etymology is studying of origins and evolution of words. It is part of semiotics, linguistics and philology. comparative semantics, morphology, pragmatics, and phonetics in order to attempt a comprehensive and chronological catalogue of all meanings and changes that a word
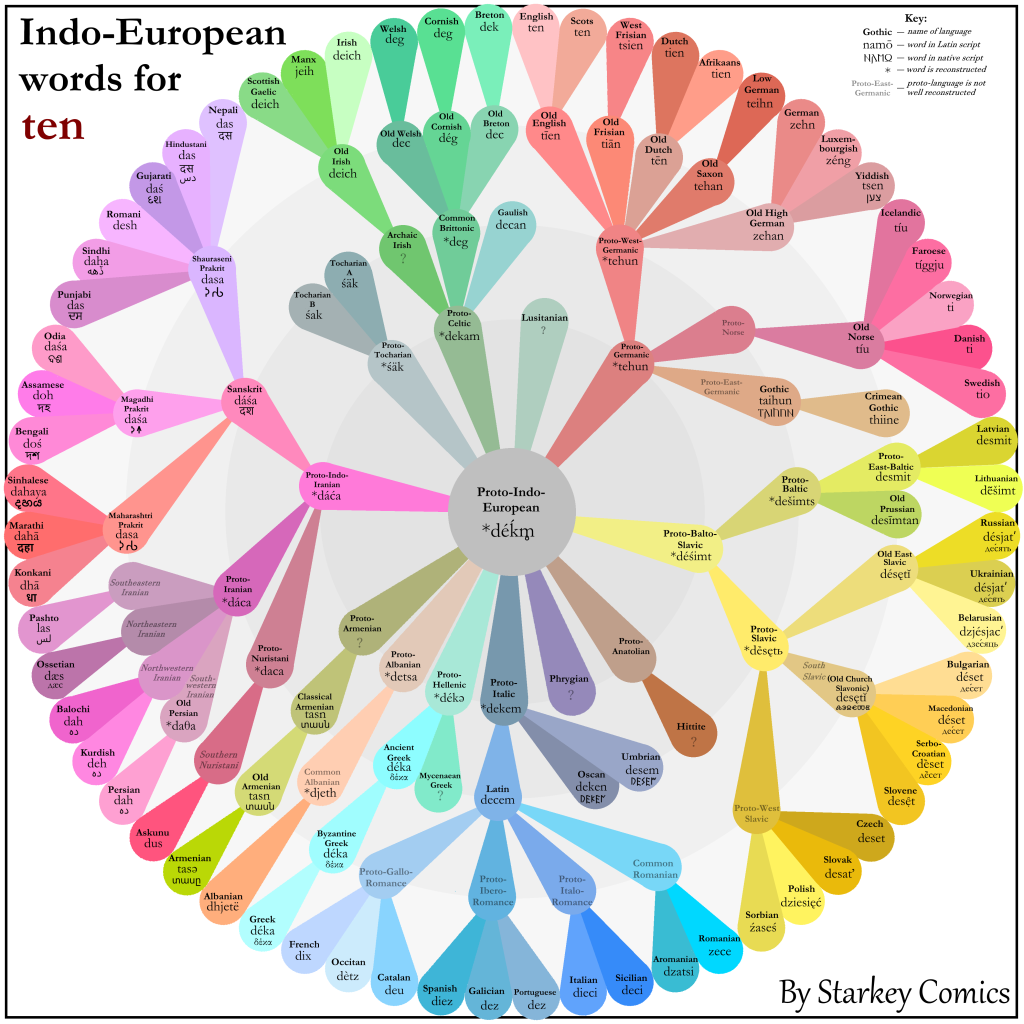
This image is the evolution of Indo-European number Ten in different languages
The word etymology is derived from the Ancient Greek word ἐτυμολογία (etymologíā), itself from ἔτυμον (étymon), meaning ‘true sense or sense of a truth’, and the suffix -logia, denoting ‘the study or logic of’.
The etymon refers to the root from which a later word or morpheme derives. For example, the Latin word candidus, which means ‘white’, is the etymon of English candid. Relationships are often less transparent, however. English toponymies such as Manchester or Leicester share different forms of a suffix that originated as the Latin castrum ‘fort’.
Reflex is the name given to a descendant word in a daughter language, descended from an earlier language. For example, Modern English heat is the reflex of the Old English hǣtu. Rarely, this word is used in reverse, and the reflex is actually the root word rather than the descendant word. However, this usage is usually filled by the term etymon instead. A reflex will sometimes be described simply as a descendant, derivative or derived from an etymon (but see below).
Cognates or lexical cognates are sets of words that have been inherited in direct descent from an etymological ancestor in a common parent language. Doublets or etymological twins or twinlings (or possibly triplets, and so forth) are specifically cognates within the same language. Although they have the same etymological root, they tend to have different phonological forms, and to have entered the language through different routes.

A root is the source of related words within a single language (no language barrier is crossed). Similar to the distinction between etymon and root, a nuanced distinction can sometimes be made between a descendant and a derivative.
A derivative is one of the words which have their source in a root word, and were at some time created from the root word using morphological constructs such as suffixes, prefixes, and slight changes to the vowels or to the consonants of the root word. For example: unhappy, happily, and unhappily are all derivatives of the root word happy. The terms root and derivative are used in the analysis of morphological derivation within a language in studies that are not concerned with historical linguistics and that do not cross the language barrier.
Source:





Leave a Reply